- 0.1:关于四叉树
- 0.2:一、使用场景
- 0.3:二、实现四叉树
- 0.4:三、根据使用场景测试
- 0.5:四、使用情景和分析
关于四叉树
定义和作用
四叉树(Quad Tree)是一种空间索引树,四叉树的每一个节点都代表着一块矩形区域。我们知道在平面直角坐标系中,平面可以被分为第一二三四象限,四叉树的每一个节点也类似,可以分裂为四个子节点,子节点在满足条件的情况下可以继续分裂,这样构成了一个四元的树状结构,就是四叉树。
四叉树的作用
通常使用树结构能够带来高效且简单的检索效果,四叉树也不例外,四叉树主要用于二维空间的检索(相应的,三维空间可以了解下八叉树,理论上来讲,对于N维空间的检索可以根据这个原理构成2^N叉树,此外多维空间的检索还有kd树)。
四叉树的操作
1、节点分裂
当满足特定条件时,为了获得更好的检索效率,四叉树的节点会发生分裂,分裂的做法是:以当前节点的矩形为中心, 划分出四个等大的矩形,作为四个子节点,每个节点深度=当前节点深度+1,根节点深度为0;并且将当前节点的元素重新插入到对应的子节点。
2、插入元素
1)平面的元素多种多样,点,线,图形,但都能够做一个统一,第一步都是要找出图形所覆盖的节点,这里以矩形为例
2)从根节点开始,如果当前节点无子节点,将元素插入到当前节点。如果存在子节点K,并且元素能够完全被子节K点所“包围”,就将元素插入到子节点K,对于子节点K进行上述递归操作;如果元素跨越了多个子节点,那就将元素存储在当前节点
3)如果某一节点元素超过特定值,并且深度小于四叉树允许的最大深度,分裂当前节点。
3、检索
1)对于给定检索区域,从根节点起,如果检索区域与当前节点有交集,返回当前节点的所有元素。
2)如果当前节点还有子节点,递归检索与检索区域有交集的子节点。
一、使用场景
我们有一个很大的场景,场景有许许多多的敌人。红色的点代表是玩家,黑色的点代表是敌人。在这样的一个大量敌人的情景下,我们不可能在玩家或敌人寻找身边的攻击对象时穷尽所有的对象。因为我们要建立空间分区,只遍历某个对应区的对象。在图下中,红点中遍历红框中的黑点对象,其他一律不遍历,从而节约性能。
二、实现四叉树
在四叉树中我们只在叶子节点存放数据
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// <summary>
/// 叶子节点类,负责坐标与数据的映射(T一般是gameobject即可)
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
public class QuadTreeLeaf<T>
{
private Vector2 pos;
private T refObject;
public QuadTreeLeaf(Vector2 pos, T obj)
{
this.pos = pos;
refObject = obj;
}
public T LeafObject
{
get
{
return refObject;
}
}
public Vector2 Pos
{
get { return pos; }
set { pos = value; }
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// <summary>
/// 四叉树节点
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
public class QuadTreeNode<T>
{
/// <summary>
/// 节点拥有的叶子节点
/// </summary>
protected List<QuadTreeLeaf<T>> items;
/// <summary>
/// 节点拥有的分支
/// </summary>
protected QuadTreeNode<T>[] branch;
/// <summary>
/// 节点空间最大容量,受minSize影响
/// </summary>
protected int maxItems;
/// <summary>
/// 节点空间分割的最小大小(最小宽度,高度)
/// </summary>
protected float minSize;
/// <summary>
/// 节点的空间
/// </summary>
public Rect bounds;
public QuadTreeNode(float x, float y, float width, float height, int maximumItems, float minSize = -1)
{
bounds = new Rect(x, y, width, height);
maxItems = maximumItems;
this.minSize = minSize;
items = new List<QuadTreeLeaf<T>>();
}
public bool HasChildren()
{
if (branch != null)
return true;
else
return false;
}
/// <summary>
/// 将节点空间分割4份
/// </summary>
protected void Split()
{
if (minSize != -1)
{
if (bounds.width <= minSize && bounds.height <= minSize)
{
return;
}
}
float nsHalf = bounds.height - bounds.height / 2;
float ewHalf = bounds.width - bounds.width / 2;
branch = new QuadTreeNode<T>[4];
branch[0] = new QuadTreeNode<T>(bounds.x, bounds.y, ewHalf, nsHalf, maxItems, minSize);
branch[1] = new QuadTreeNode<T>(bounds.x + ewHalf, bounds.y, ewHalf, nsHalf, maxItems, minSize);
branch[2] = new QuadTreeNode<T>(bounds.x, bounds.y + nsHalf, ewHalf, nsHalf, maxItems, minSize);
branch[3] = new QuadTreeNode<T>(bounds.x + ewHalf, bounds.y + nsHalf, ewHalf, nsHalf, maxItems, minSize);
foreach (var item in items)
{
AddNode(item);
}
items.Clear();
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据坐标获得相应的子空间
/// (返回包含该坐标的子节点)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pos"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
protected QuadTreeNode<T> GetChild(Vector2 pos)
{
if (bounds.Contains(pos))
{
if (branch != null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < branch.Length; i++)
if (branch[i].bounds.Contains(pos))
return branch[i].GetChild(pos);
}
else
return this;
}
return null;
}
/// <summary>
/// 增加叶子节点数据
/// </summary>
/// <param name="leaf"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private bool AddNode(QuadTreeLeaf<T> leaf)
{
if (branch == null)
{
this.items.Add(leaf);
if (this.items.Count > maxItems)
Split();
return true;
}
else
{
QuadTreeNode<T> node = GetChild(leaf.Pos);
if (node != null)
{
return node.AddNode(leaf);
}
}
return false;
}
public bool AddNode(Vector2 pos, T obj)
{
return AddNode(new QuadTreeLeaf<T>(pos, obj));
}
/// <summary>
///
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pos">可以是空间任意位置,只是根据这个位置找到所在的空间去删除对象</param>
/// <param name="obj"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool RemoveNode(Vector2 pos, T obj)
{
if (branch == null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < items.Count; i++)
{
QuadTreeLeaf<T> qtl = items[i];
if (qtl.LeafObject.Equals(obj))
{
items.RemoveAt(i);
return true;
}
}
}
else
{
QuadTreeNode<T> node = GetChild(pos);
if (node != null)
{
return node.RemoveNode(pos, obj);
}
}
return false;
}
public bool UpdateNode(Vector2 pos, T obj)
{
// TODO 参找RemoveNode
return false;
}
/// <summary>
/// 得到在一个Rect内的所有数据(根据两个rect是否有交集)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="rect"></param>
/// <param name="nodes"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int GetNode(Rect rect, ref List<T> nodes)
{
if (branch == null)
{
foreach (QuadTreeLeaf<T> item in items)
{
if (rect.Contains(item.Pos))
{
nodes.Add(item.LeafObject);
}
}
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < branch.Length; i++)
{
if (branch[i].bounds.Overlaps(rect))
branch[i].GetNode(rect, ref nodes);
}
}
return nodes.Count;
}
/// <summary>
/// 根据坐标得到坐标附近节点的数据(圆心+半径)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="pos"></param>
/// <param name="ShortestDistance">离坐标最短距离</param>
/// <param name="list"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int GetNodeRecRange(Vector2 pos, float ShortestDistance, ref List<T> list)
{
float distance;
if (branch == null)
{
foreach (QuadTreeLeaf<T> leaf in this.items)
{
distance = Vector2.Distance(pos, leaf.Pos);
if (distance < ShortestDistance)
{
list.Add(leaf.LeafObject);
}
}
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < branch.Length; i++)
{
float childDistance = branch[i].bounds.PointToBorderDistance(pos);
if (childDistance < ShortestDistance * ShortestDistance)
{
branch[i].GetNodeRecRange(pos, ShortestDistance, ref list);
}
}
}
return list.Count;
}
public void DrawBounds()
{
if(HasChildren())
{
foreach(var i in branch)
{
i.DrawBounds();
}
}
else
{
Gizmos.color = Color.black;
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(bounds.center, bounds.size);
}
}
}
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// <summary>
/// Rect的扩展方法类
/// </summary>
public static class RectExtension
{
/// <summary>
/// 计算点到Rect的border的距离,若点在Rect内则返回0
/// </summary>
/// <param name="rect"></param>
/// <param name="pos"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static float PointToBorderDistance(this Rect rect, Vector2 pos)
{
float xdisance;
float ydisance;
if (rect.x <= pos.x && pos.x <= rect.xMax)
{
xdisance = 0;
}
else
{
xdisance = Mathf.Min(Mathf.Abs(pos.x - rect.xMax), Mathf.Abs(pos.x - rect.x));
}
if (rect.y <= pos.y && pos.y <= rect.yMax)
{
ydisance = 0;
}
else
{
ydisance = Mathf.Min(Mathf.Abs(pos.y - rect.yMax), Mathf.Abs(pos.y - rect.y));
}
return xdisance * xdisance + ydisance * ydisance;
}
}
三、根据使用场景测试
1.构建一棵树。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// <summary>
/// 构建四叉树
/// 挂在任意物体上,也可以在其他代码中实现初始化
/// </summary>
public class TreeManager : MonoBehaviour
{
public static QuadTreeNode<GameObject> quadRoot = new QuadTreeNode<GameObject>(-5, -5, 10, 10, 2,3);
}
2.给每个需要加入树的物体挂载该脚本。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class QuadTreeObject : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
//向树中插入该物体
TreeManager.quadRoot.AddNode(new Vector2(transform.position.x, transform.position.z), this.gameObject);
}
}
3.Player脚本,使用查找圆心加半径的方式找到区域内的物体。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
/// <summary>
/// 查找距离Player指定范围内的物体
/// </summary>
public class Player : MonoBehaviour
{
[Range(1,5)]
public float detectRange = 1f;
private List<GameObject> detectedGameObjects = new List<GameObject>();
[Header(header: "材质")]
[SerializeField]
private Material outMaterial;
[SerializeField]
private Material inMaterial;
private Vector3 oldPos;
private bool hasMoved = false;
private void Start()
{
oldPos = transform.position;
}
private void Update()
{
hasMoved = oldPos != transform.position;
oldPos = transform.position;
//有位置变化再进行查询
if(hasMoved)
{
foreach (var i in detectedGameObjects)
{
i.GetComponent<Renderer>().material = outMaterial;
}
detectedGameObjects.Clear();
TreeManager.quadRoot.GetNodeRecRange(new Vector2(transform.position.x, transform.position.z), detectRange, ref detectedGameObjects);
foreach (var i in detectedGameObjects)
{
i.GetComponent<Renderer>().material = inMaterial;
}
}
}
private void OnDrawGizmos()
{
if(Application.isPlaying)
{
Gizmos.color = Color.black;
//在QuadTreeNode中使用的是vector2,绘制时在xy平面所以需要旋转90度。
Gizmos.matrix = Matrix4x4.TRS(Vector3.zero, transform.rotation, Vector3.one);
TreeManager.quadRoot.DrawBounds();
Gizmos.color = Color.red;
Gizmos.matrix = Matrix4x4.identity;
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(transform.position, detectRange);
}
}
}
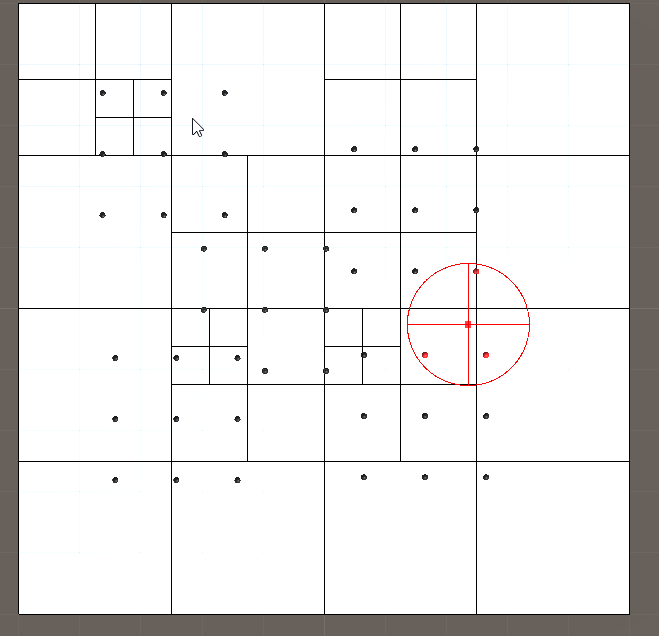
四、使用情景和分析
如果在相同位置有多个物体存在,一定要设置好Node的最小尺寸,否则会无限分割。
目前只是实现了数据的插入、删除和查询,还有物体移动后树的更新没有实现,如果一个物体横跨两个节点的情况也没有处理。
适用的情况是物体数量很大(至少要超过100个,否则暴力遍历就可以了)。
物体分布均匀的情况下,我们可以采用另外一种方式会更有效,那就是对区域进行网格划分,用二维数组的下标代表区域编号。
如果遇到要划分的区域不规则,我们也可以使用多个树进行拟合。
